If you've ever wondered why some people carry weight in a different way to others, you're actually wondering about metabolism and body types.
The concept of metabolic types categorizes individuals into three main body types: ectomorphs, mesomorphs, and endomorphs.
These body types, also known as somatotypes, are characterized by distinct physical traits and tendencies related to metabolism, body composition, and energy utilization.
Ectomorphs have a naturally lean body type with a fast metabolism, mesomorphs are naturally muscular and responsive to training, while endomorphs have a higher body fat percentage and a harder time trying to lose weight.
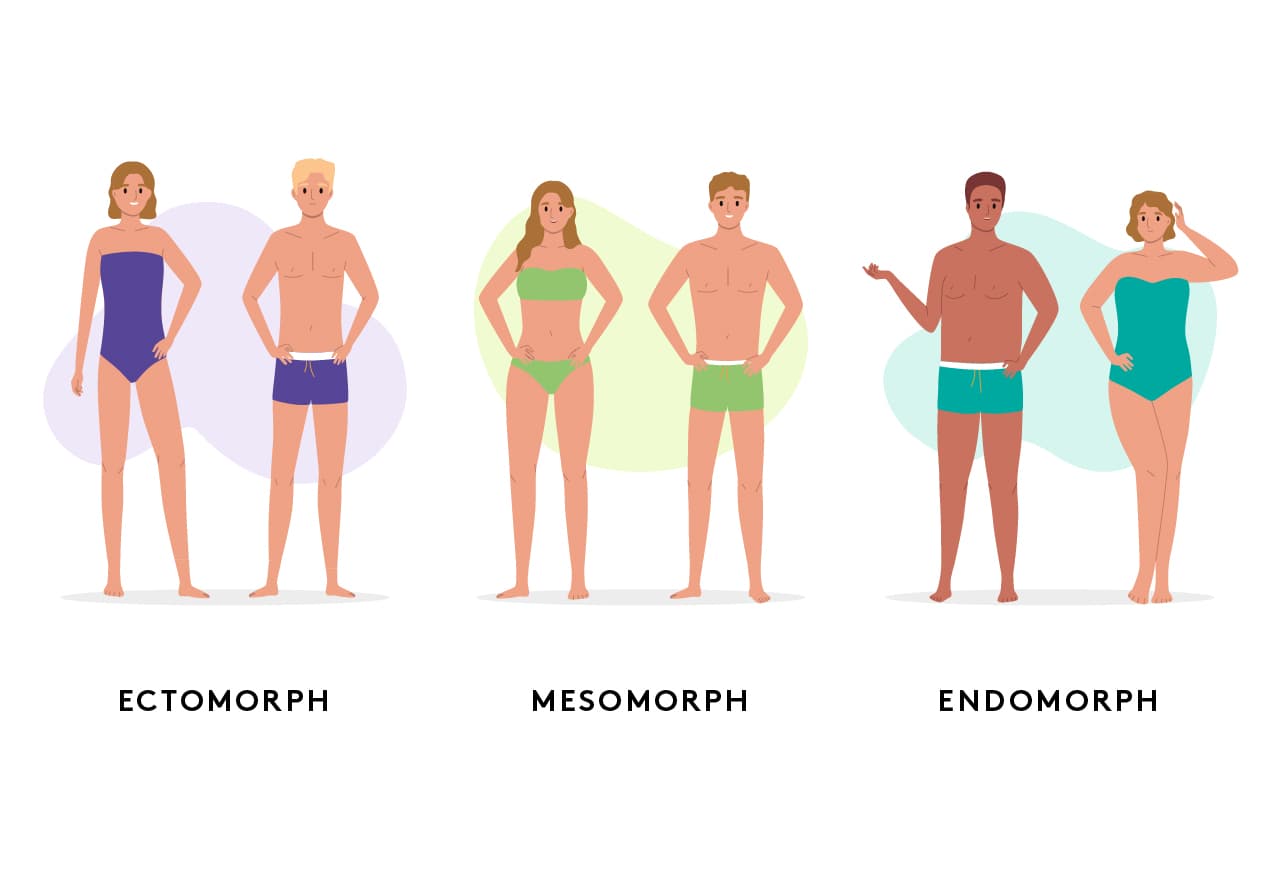
So which of the metabolic body types are you: ectomorph, mesomorph or endomorph?
Or perhaps a combination defines your body type best.
By understanding your own metabolic type, you can optimize your personal fitness regimen, tailor your diet and fine-tune your ability to lose and gain fat and muscle tissue.
Identifying your own body type can help you choose foods, exercise routines and supplements that will yield the best results for health and body composition -- whether you're aiming for weight loss, muscle gain or general fitness.
Essentially, knowledge of your body type enables you to you best accentuate positive characteristics and downplay negative ones on your way to health and well-being.
In this article, we will define the three main metabolic body types. We will give recommendations for each body type, with tips for diet, exercise and supplementation. Let's get to it!
What is Metabolism?

Since we are delving into metabolic types, let's first take a look at metabolism.
Metabolism is the catchall term given to the many bodily processes that combine to sustain life in humans and other living creatures. It is sometimes boiled down to energy processes, including those that break down foods and convert them into energy.
Simply put, metabolism is a key factor that keeps our body functioning and working as it should!
Your basal metabolic rate (BMR) refers to the number of calories your body uses to carry out the above mentioned bodily functions as well as many other functions. When you hear terms like "fast metabolism" and "slow metabolism", they are referring to BMR.
There are a number of factors which can influence how your metabolism works, which include:
- Sex: Men tend to burn more calories (have faster metabolisms) than women due to typically having less body fat and more muscle mass.(1)
- Age: Children have a lot of energy for a reason - your metabolism works much faster the younger you are. As you age, your metabolism slows down due to typical muscle loss and fat gain, which slows down the process of burning calories.
- Body size and composition: Larger individuals and those with more muscle mass are prone to burning more calories, even at rest. However, older and larger people who have excess body fat tend to have slower metabolisms.
- Physical activity: How much you move (the energy you burn) and your exercise habits can greatly influence your metabolic rate. Movement = energy burn, especially any movement outdoors!
The different metabolic body types have different metabolic functioning. In turn, metabolism determines how your body converts food to fuel, and how easy or hard of a time you will have losing weight.
What is Your Metabolic Type?
Metabolic body types fall into three main categories, but they can also present as combinations.
For the most part, you may recognize your body type due to the characteristics associated with it, especially in terms of body composition.
Let's now take a closer look at the three main body types, as well as some health and fitness tips that correspond to each one.
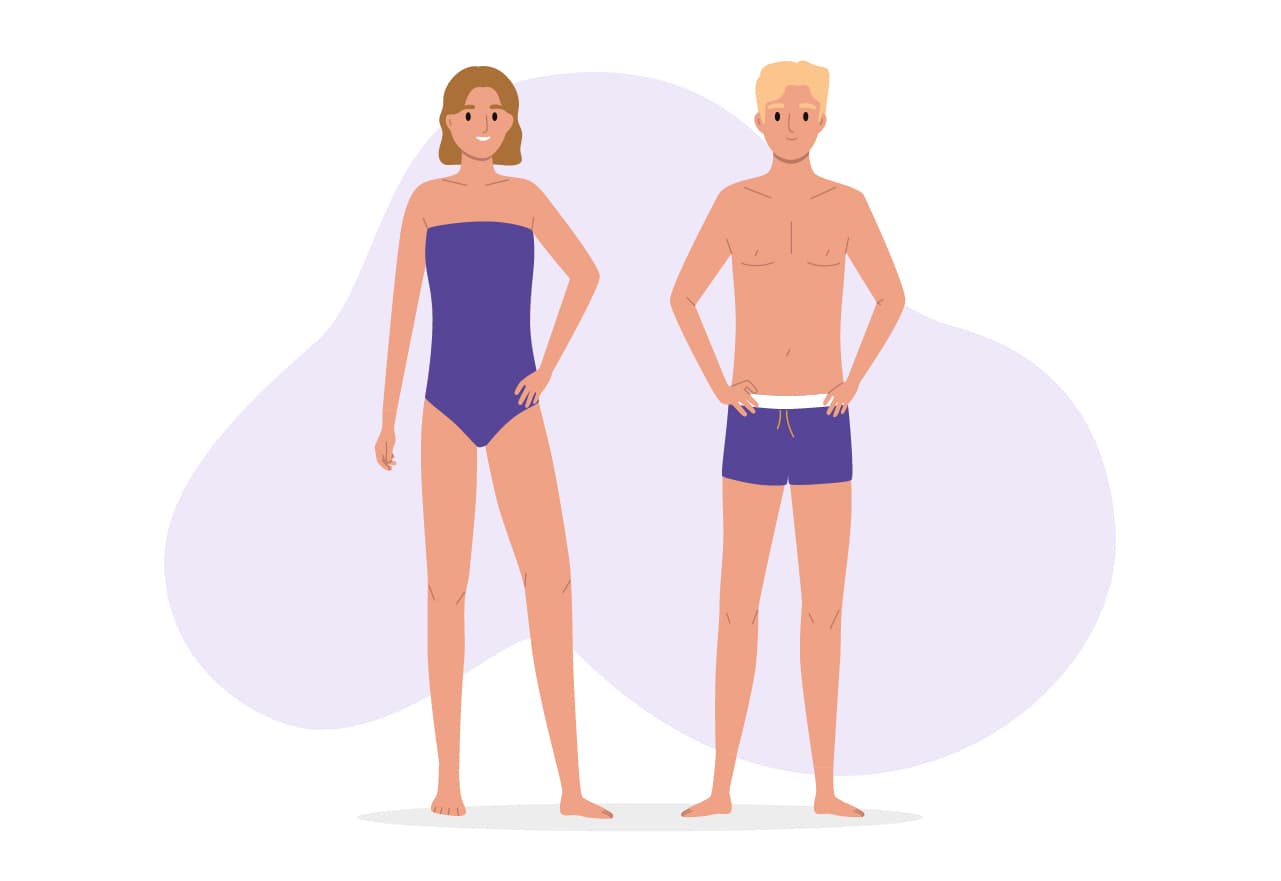
Ectomorph
The ectomorph's body frame characteristics:
- Slender, lean and may be taller
- Narrower hips and shoulders
- Smaller muscles and little fat; low body fat percentage
- Struggle to gain muscle or fat
- Easier to lose weight when needed
- Faster metabolism (basal metabolic rate)
Ectomorph diet tips
Ectomorphs, with their thin metabolic body type, may desire to pack on more muscle mass. Dietary changes can help support ectomorphs' body composition goals.
If you have an ectomorph body type, consider prioritizing calorie-dense foods like healthy fats and complex carbs.
Ectomorphs have a higher tolerance for carbohydrates and can handle a relatively high carb intake without gaining excessive fat. This is important because carbs promote sustained energy levels and facilitate protein uptake, which in turn promotes muscle growth.

Ectomorphs are also advised to consume enough protein rich foods to support healthy muscle development.
Low-calorie foods are generally discouraged for ectomorphs who are striving for a larger build. People with this metabolic body typically want to maintain or gain mass, not lose weight.
The ectomorph body type may also benefit from greater eating frequency; five or six snacks and meals per day to gain weight.
Ectomorph workout routines
In general, ectomorphs will be interested in adding muscle mass to compensate for their naturally slight body type. Ectomorphs should focus on a workout routine that emphasizes muscle building and strength, including targeted lifts for weaker upper body muscles, using relatively heavy weights.

Incorporate compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses to target multiple muscle groups and bulk up. Opt for moderate to heavy lifting with short rest periods to stimulate growth in large muscle groups. Prioritize progressive overload by gradually increasing weights or reps.
Those with ectomorph bodies should avoid excessive cardio exercise if they're looking to bulk up. And instead focus energies on strength training. Since ectomorphs do not gain muscle easily, allowing sufficient recovery time and sleep is key for success.
Supplements for Ectomorphs
Ectomorphs aiming for muscle gain might benefit from certain sports nutrition supplements that can help drive peak performance, recovery and anabolic growth.
- Protein supplements provide essential amino acids for muscle recovery and growth
- A good pre-workout supplement to drive the training intensity that's required for muscle gains
- Creatine monohydrate enhances strength and muscle-building efforts during high-intensity workouts.
- Carbohydrate supplements aid in meeting increased energy needs, supporting weight gain.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (plant-based, ideally) to soothe muscles & joints and promote recovery after training (2)
- A high-quality multivitamin to ensure proper micronutrient balance
- A natural sleep supplement to accelerate recovery and maximize muscle growth

Mesomorph
The mesomorph's body type characteristics:
- Naturally Athletic
- Lean and muscular
- Rectangular body shape; broad shoulders
- Balanced, healthy weight: Not overweight, nor underweight
- Medium bone structure
- Can gain and lose body mass with relative ease
- Efficient and balanced metabolic performance
The mesomorph metabolic body type typically gains weight and muscle easily. It is a common bodybuilder's body type and naturally athletic body, suggested to perform better in weight lifting and sports.(3)
Mesomorph body types tend to have a balanced metabolism, allowing them to maintain a trim body composition while still gaining lean muscles mass.
Their ability to efficiently use nutrients can support efficient muscle growth, but they still need to manage their diet to avoid excessive fat gain.
Mesomorph diet tips
Mesomorphs' muscular and athletic metabolic body type is easier to maintain. However, portion control is still essential to avoid excessive weight gain.
Mesomorphs are genetically gifted with a desirable body composition. This can sometimes lead to a false sense of security: They may overindulge in sweets, starchy carbs or processed foods because they believe they can "get away with it," so to speak.

While unhealthy foods may not pack on pounds easily with the mesomorph body type, they can still raise risk for health concerns, as with other body types.
Further, as mesomorphs age and metabolism slows, their body type may become less forgiving when it comes to high carb intake and consuming junky foods.
Mesomorph workout routines
The mesomorph body type responds well to a workout routine that includes both strength training and cardiovascular exercise. They can capitalize on their naturally athletic body type with a versatile fitness routine.
If you are a mesomorph metabolic type, focus on a mix of strength training and cardio. Utilize progressive resistance to maintain muscle growth and strength gains. Incorporate a variety of exercises to prevent plateaus and stave off boredom.

Flexibility practices like yoga and pilates can also help mesomorphs take their physique to the next level.
Experimenting with different training styles like circuit training or plyometrics can also help mesomorphs to keep their workouts engaging.
It is important for mesomorphs to high-intensity workouts with adequate recovery time. Even though they gain muscle easily, mesomorphs can be prone to overexertion and injury in the gym.
Mesomorphs should also maintain fitness routines like other body types. Although they may not need to work as hard for fitness results, healthy and fitness goals may be harder to maintain as they age and their metabolisms begin to slow down.
Supplements for Mesomorphs
Mesomorphs can consider supplements that enhance their muscle-building and performance potential.
- Protein powder provides quick-digesting protein for post-workout recovery.
- Creatine monohydrate supports strength and muscle gains during high-intensity workouts.
- Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) aid in muscle recovery and reduce muscle breakdown.(4)
- Pre-workout supplements with moderate-dose caffeine and nitric oxide precursors can boost energy and enhance exercise performance.
Ectomorphic and endomorphic body types tend to strive for the healthy mesomorphic ideal.
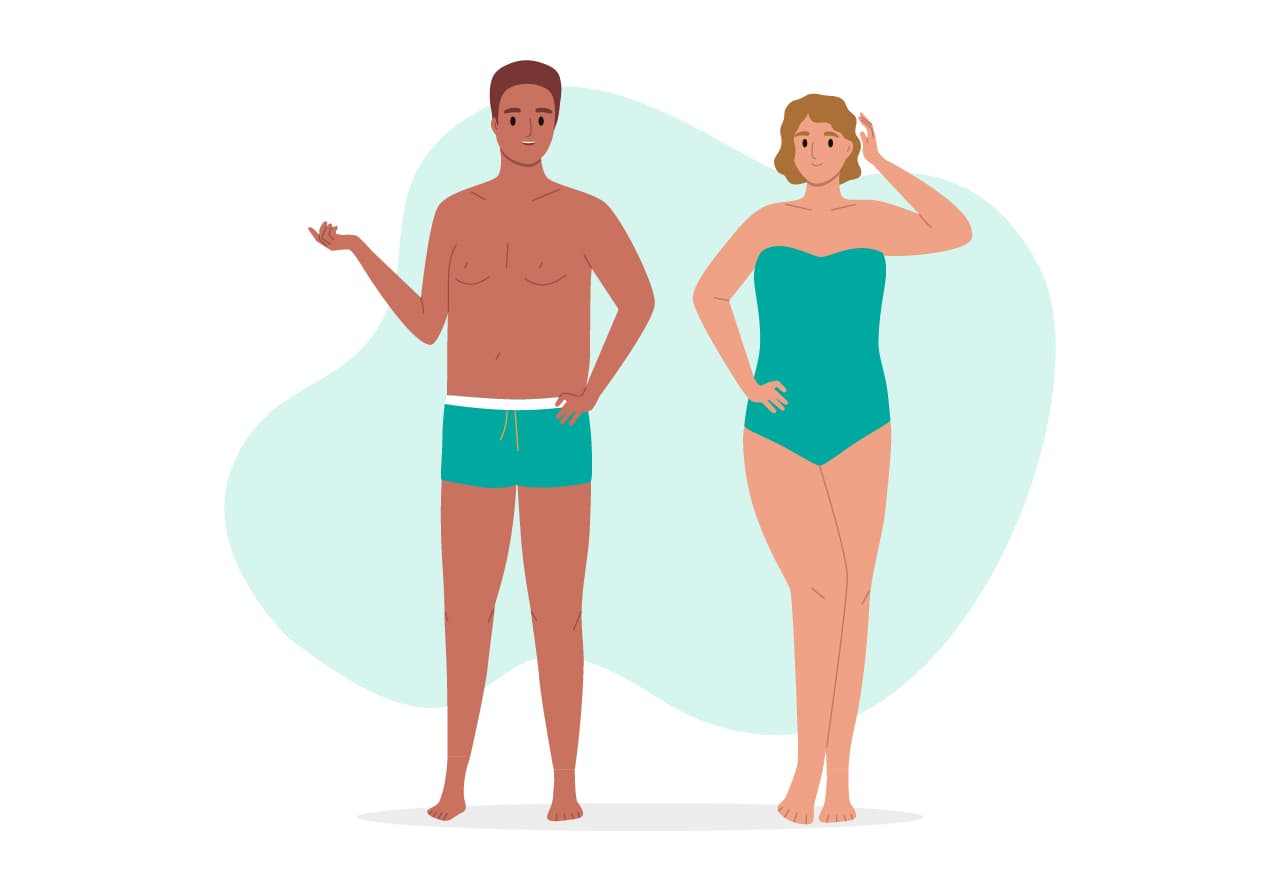

Endomorph
- The endomorph metabolic body type characteristics:
- Soft, round body
- Medium to short stature
- Larger amounts of both muscle and fat on frame
- Gains fat easily; more excess fat, more difficult to lose weight
- Larger bone structure
- Narrow shoulders, wider hips and larger midsection
- Thicker arms; strong leg muscles and thick lower body
- Slower metabolism
The endomorph body is naturally strong but also tends to pack on extra body fat easily. Endomorph body is softer and rounder, with thicker arms and legs, along with larger bone structure that carries more overall body fat.
They often find it easy to gain weight but challenging to lose weight. As a result, endomorphs be mindful of their calorie intake and slow metabolism.
Building muscle can be more challenging for the endomorph body type due to their tendency to store extra calories as fat. However, with the right diet and exercise regimen, the endomorph can overcome the body's natural inclination towards more body fat, and achieve a healthy body composition.
Endomorph diet tips
Endomorph body type, characterized by a tendency to gain fat easily, should focus on a diet that controls calorie intake to support weight loss. Emphasizing nutrient rich whole foods like lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains can aid this body type in weight loss efforts.
High fiber foods, especially those that supply prebiotic fiber, are key for the endomorph metabolic body type, in part because they are suggested to assist with weight loss efforts.(5)

Some prebiotic foods for endomorphs to add to their diets include:
- Chicory Root: Best for endomorphs overall. This root supplies Inulin-FOS fiber clinically shown to boost metabolism and enhance nutritional status.
- Apples
- Bananas
- Jerusalem Artichokes
- Oats
Portion control is crucial for endomorphs, as they might have a slower metabolism. A low carb eating plan -- combined with adequate fiber intake -- can help endomorphs to stabilize blood sugar levels and avoid excessive fat gain.
Endomorph workout routines
Endomorphs should focus on a well-rounded exercise program that combines resistance training and cardiovascular workouts.
Incorporate compound movements like squats, lunges, and rows to boost metabolism and build muscle. Include high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to burn calories efficiently and encourage healthy weight loss.

Strength training also helps shift soft-and-round body composition to muscular. This in turn can help speed up the endomorph body's slow metabolism, and steer body composition towards the mesomorph body ideal.
It is important that endomorphs prioritize consistent exercise to aid in weight management.
Incorporate flexibility and mobility exercises to enhance overall fitness. Maintain a balanced approach, avoiding excessive cardio that might hinder muscle preservation. Adequate sleep and proper nutrition are key for recovery.
Supplements for Endomorphs
Endomorphs can benefit from supplements that support their metabolism and weight management efforts.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (found fish oils, healthy oils from flaxseed, or in vegan algae supplements) can help reduce inflammation and promote healthy fat loss.
- Fiber supplements, especially prebiotics, aid in controlling appetite and stabilizing blood sugar levels. Very helpful for endomorphs who gain fat easily to curb cravings and limit calorie intake.
- Vitamin D supports overall health and can impact metabolism. Get it in a high-quality multivitamin or in a more dedicated vitamin D supplement.
- Joint soothers. Endomorph body types tend to have more inflammation, including achy joints. Soothing botanical extracts in joint supplement form can help.
When considering these metabolic types, remember that they are just one piece of the puzzle.
Factors like genetic makeup, hormonal balance, sleep, stress, and overall health also contribute significantly to an individual's physique and metabolism.
Therefore, it's important to approach health and fitness holistically, taking into account various elements that influence well-being.
It's also important to understand that these metabolic types are generalizations, and most people exhibit a combination of traits from multiple types.
This typically means one dominant body type that is influenced by a secondary body type. For example:
- Ecto-endomorph body type: thin upper bodies, but fat accumulates around the lower body including posterior, hips and thighs;
- Endo-ectomorph body type: "Apple shaped" body where fat tends to accumulate around the midsection while limbs and extremities remain thin
Additionally, while metabolic type might provide some insights, it's not a strict determinant of how someone should eat or exercise.
Tailoring nutrition and exercise plans to one's goals, preferences, and individual responses is crucial.
Not sure which type of metabolism you have? Learn more about your metabolic type here.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the three metabolic body types — ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph — provide a basic framework for understanding how individuals might respond to different diets and exercise routines.
However, individual variations and genetic makeup still play a substantial role in shaping an individual's body composition and metabolism.
It's wise to use these concepts as a starting point but to customize approaches based on individual health and fitness goals and needs.
Consulting with healthcare or fitness professionals can provide personalized guidance for optimizing health and fitness outcomes.
References
1. Wu BN, O'Sullivan AJ. Sex differences in energy metabolism need to be considered with lifestyle modifications in humans. J Nutr Metab. 2011;2011:391809. doi: 10.1155/2011/391809. Epub 2011 Jun 6. PMID: 21773020; PMCID: PMC3136178.
2. Thielecke F, Blannin A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Sport Performance-Are They Equally Beneficial for Athletes and Amateurs? A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2020 Nov 30;12(12):3712. doi: 10.3390/nu12123712. PMID: 33266318; PMCID: PMC7760705.
3. Ryan-Stewart H, Faulkner J, Jobson S. The influence of somatotype on anaerobic performance. PLoS One. 2018 May 22;13(5):e0197761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197761. PMID: 29787610; PMCID: PMC5963773.
4. VanDusseldorp TA, Escobar KA, Johnson KE, Stratton MT, Moriarty T, Cole N, McCormick JJ, Kerksick CM, Vaughan RA, Dokladny K, Kravitz L, Mermier CM. Effect of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation on Recovery Following Acute Eccentric Exercise. Nutrients. 2018 Oct 1;10(10):1389. doi: 10.3390/nu10101389. PMID: 30275356; PMCID: PMC6212987.
5. Ferrarese R, Ceresola ER, Preti A, Canducci F. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics for weight loss and metabolic syndrome in the microbiome era. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Nov;22(21):7588-7605. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16301. PMID: 30468509.














