Remember when coconut oil used to be all the rage? Well, more recently, it's been replaced by its cousin — MCT oil. And there's a pretty good reason behind why it's so popular.
Whether you're looking to build muscle, lean out, or just increase your energy and athletic performance, there's a good chance that MCT can help out.
And while some health benefits of MCT may be over-hyped, there is a growing body of evidence to suggest that MCT oil can be a useful dietary addition for bodybuilders, weightlifters, and other athletes.
In lieu of that, let's explore the benefits of MCT oil for training and whether it should be a part of your pre-workout, post-workout, or both!
What Is MCT Oil?

MCT: Medium-Chain Triglycerides
Medium-chain triglycerides, commonly referred to as MCTs, are a type of fat extracted from either coconut oil or palm kernel oil but also naturally found in certain dairy products like goat's milk and even human breast milk.
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are naturally present in food sources, along with short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), but in 100% pure MCT oil, the MCTs are extracted through a process called fractionation to produce a pure medium-chain fat product.
To understand the role of MCT oil in health, it's important to know about the three types of fatty acids.
Understanding Fatty Acids and MCT
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
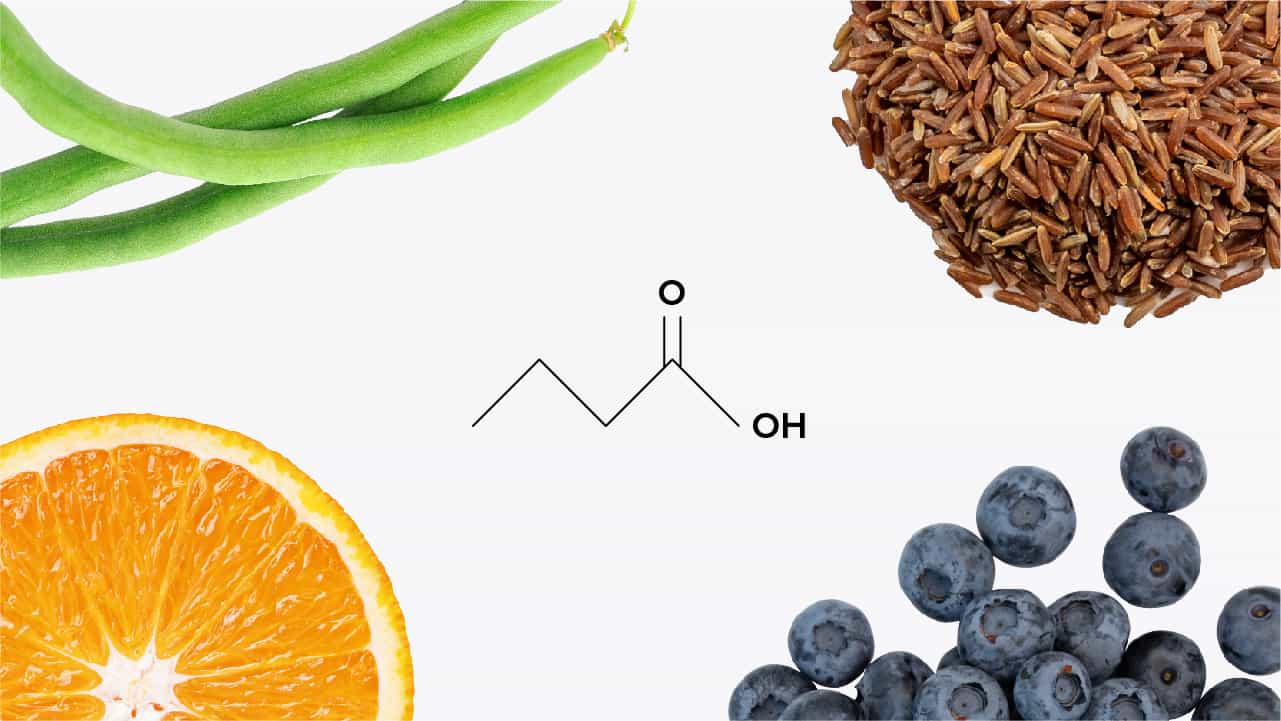

Short-chain fatty acids contain fewer than 6 carbons. These fatty acids are primarily produced when the beneficial bacteria in your gut ferment dietary fibers found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. SCFAs play a crucial role in gut health and have anti-inflammatory effects.
Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
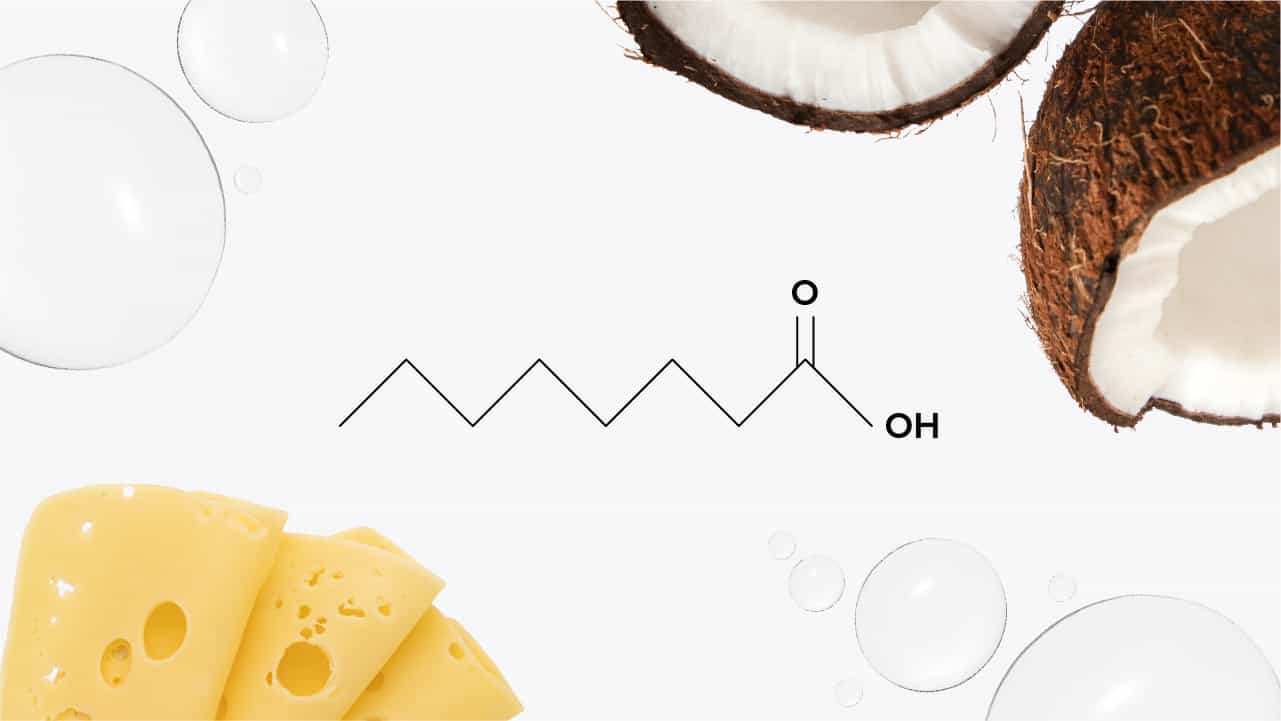
Medium-chain fatty acids contain 6-12 carbons and are found in foods like coconut oil, palm oil, and dairy products. Unlike other fats, MCFAs are absorbed directly into the bloodstream and converted into energy more quickly, making them a preferred energy source during high-intensity workouts or for those following a ketogenic diet.
Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
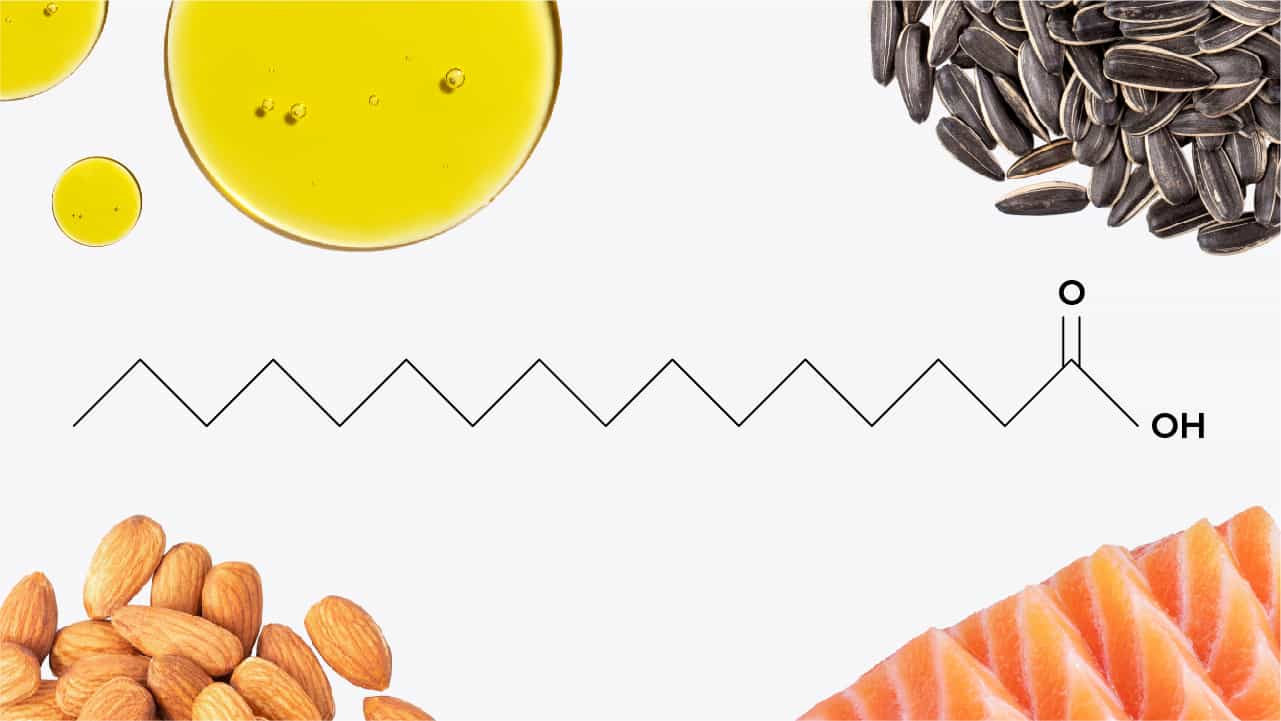

Long-chain fatty acids contain 13-21 carbons and are the most common type of fat in the diet. Found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, LCFAs are essential for brain fuel and energy but must be metabolized more slowly than MCFAs, making them a more prolonged energy source.
The Specifics of MCTs
The Four Types of MCTs
There are four different types of MCTs: caproid acid (C6), caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), and lauric acid (C12), but many of the benefits of MCT oil come from only two—C8 and C10 triglycerides, with few coming from lauric acid; lauric acid is the main fat found in coconut oil, and while it possesses some similar properties to MCT oil, it's metabolized differently.
But when you're looking to reap all the health-promoting benefits of MCT oil, you want to be looking for one that contains only C8 or C10 carbon—like Performance Lab MCT. It's fast-acting metabolic fuel for peak mind and body performance.
Performance Lab MCT
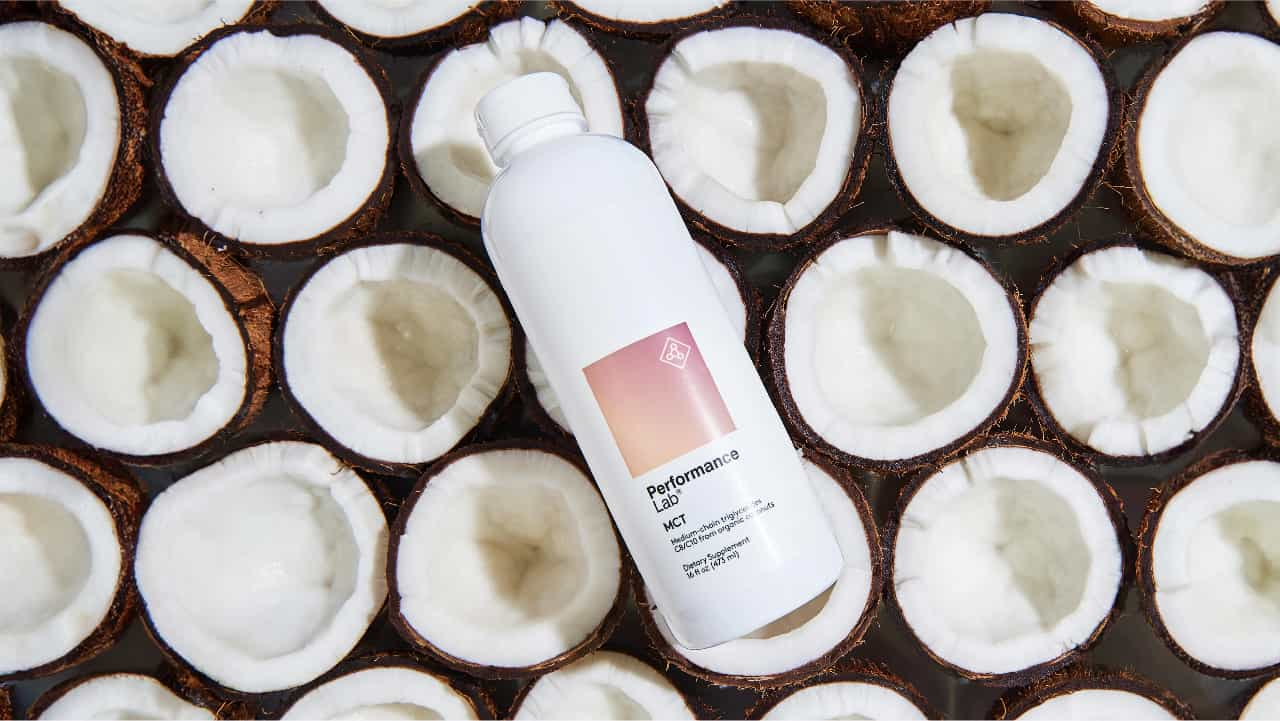

Derived from C8+C10 MCTs only, Performance Lab MCT oil is the ultimate upgrade.
Not to mention it's sourced from 100% organic non-GMO coconuts, cold-extracted with hexane-free technology, and 3X distilled for purity to deliver quick, convenient mental energy and enhanced results across all fat loss programs.
The Benefits Of Adding MCT Oil Into Your Diet
Want to know why we hype up MCT for being part of a healthy diet?
Here's the lowdown:
1 .Quick and clean energy — One reason MCT oil is so popular (and prized on the keto diet) is its ability to bypass the digestive system during metabolism and go directly towards energy production to support optimal energy levels.
Compared to LCFAs incorporated into chylomicrons before entering the lymphatic system and systemic circulation , MCTs are degraded into three fatty acids, and a glycerol molecule or are absorbed fully intact. Whereas LCFAs must enter lymphatic circulation before being absorbed, MCTs are absorbed directly from the small intestine and transferred into portal circulation for transport to the liver.
In the liver, they provide an immediate source of energy and a substrate for ketone production. 1 Additionally, MCTs don’t require the presence of bile or pancreatic enzymes for digestion and do not require carnitine as a shuttle to enter the mitochondria for energy production. 2
2. Metabolic Efficiency and Fat Burning — Adding MCT oil to your diet can enhance metabolic efficiency, turning your body into a fat-burning machine which can contribute to weight loss. MCT oil helps in burning fat by jumpstarting metabolism and accelerating fat-burning processes.
By enhancing metabolic efficiency, MCT oil helps to reduce fat storage and promote the use of stored fat for energy during training sessions. 3
MCT oil has been shown to increase fat burning and reduce fat storage, which could help manage the symptoms of diabetes. This is especially beneficial for individuals following a low carbohydrate diet, as it supports the body in maintaining energy levels without needing to rely on glucose from carbs.
3. Improve insulin sensitivity — While this one may not be the first association you make with MCT, studies show potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic properties. These triglycerides are broken down into free fatty acids (FFA), which enhance beta-cell secretion of insulin in response to glucose. But the MCT fats also contribute less insulinotropic signaling and are linked to lower levels of inflammation and improved insulin sensitivity.
MCTs have also been associated with enhanced mitochondrial beta-oxidation and biogenesis, increased mitochondrial respiratory capacity, and less oxidative stress. 4
4. Enhance training and Exercise Performance — Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, are the primary energy drivers for skeletal muscle contraction. Studies show that consuming MCT could increase mitochondrial biogenesis and therefore positively affect exercise performance.
One study, specifically, found that MCT upregulated several factors involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and the respiratory chain, suggesting that MCT improves skeletal muscle function by inducing mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolism under high-temperature conditions—like those that are brought on by exercise. 5
Basically, more mitochondria means more energy and better performance. By incorporating MCT oil into your pre-workout routine, you can ensure your energy levels are optimized for your training sessions, allowing for increased fat burning and enhanced athletic performance.
5. Appetite Suppression — The healthy fat in MCT oil helps in suppressing appetite by raising ketones, influencing appetite-controlling hormones, and stabilizing blood sugar, which reduces energy highs and lows from eating carbs.
When To Take MCT Oil: Pre or Post-Workout

Pre-Workout
If you’re looking to kick up your energy before a fasted workout, MCT may be a great addition. MCTs are known to readily hydrolyze into fatty acids that are metabolized quicker through beta-oxidation than long-chain fatty acids.
Due to their rapid metabolism, MCTs could be beneficial for boosting exercise performance by supplying faster and cleaner energy. 6 Additionally, MCTs can improve gut health by enhancing bacterial gut health and digestion efficiency, contributing to a healthier intestinal ecosystem.
One study looked at effects of MCT supplementation on exercise performance in recreational athletes given food containing 6g of either MCT or LCT for two weeks. 7
It’s suggested that the satiety of MCT oil may be attributed to the release of specific hormones, including cholecystokinin (CCK), peptide YY, gastric inhibitory peptide, neurotensin, and pancreatic polypeptide.
And studies also show that it may increase energy expenditure by influencing thermogenesis, thereby helping to boost weight loss. 8
And like we said before, MCT has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which means that your cells are actually getting the energy and nutrients they need to repair themselves and grow. So, theoretically, better nutrient absorption should translate to better gains, right?
How To Use MCT Oil

Really, there's no right or wrong time to consume MCT. But if you're looking for quick and easy ways to incorporate it into your diet, here are some ideas:
-
Add it to a smoothie or shake — Smoothies and shakes are an underrated way to load up on nutrients. Why not take it a step further and add MCT as your fat source to boost energy and increase nutrient absorption?
-
Use it in a salad dressing — Replace your normal go-to extra virgin olive oil with MCT for an equally tasty fat-burning dressing. Because MCT is tasteless, it blends well with any flavors!
Click here for our Asian Slaw Salad with MCT dressing recipe.
-
Blend it into your coffee — Training fasted? Throw a tablespoon of MCT into your coffee and whiz it up for a quick hit of caffeine alongside Pre Lab Pro for the perfect pre-workout combo.
-
Take it straight — Straight off a spoon is another no-fuss way to get your dose of MCT.
Final Thoughts
Long story short, MCT is a great add-in pre-workout or post-workout. Whether you're looking for more energy or fat loss, it can push you in the right direction by providing rapid-source fat to power you through all of your daily activities.
Keep in mind that MCT shouldn't be a sub for all of your fats. Because they don't contain any essential fatty acids, you'll still want to ensure you're consuming other fat sources along with it.
But the point here is that as long as you're doing everything else right in terms of diet and supplementation, MCT consumption should improve training results and fat loss.














